Electronic data interchange (EDI) is the concept of businesses electronically communicating information that was traditionally communicated on paper, such as purchase orders and invoices. EDI can be defined as the transfer of structured data, by agreed message standards, from one computer system to another without human intervention.
By moving from a paper-based or offline technology exchange of business document exchange to one that is electronic, businesses enjoy major benefits such as reduced cost, increased processing speed, reduced errors and improved relationships with business partners.
To provide an example to illustrate EDI, let us take a Procure-to-Pay business process commonly used across most industries where Buying organizations procure products, raw materials, finished goods, services from Supplying organizations.
Figure A refers to a typically manual process that uses offline technologies as a method to get a purchase order created by the buying organization into the system of the Supplying organization and a subsequent invoice triggered from the supplying organization
Manual Based Business Process Workflow Using Offline Technologies
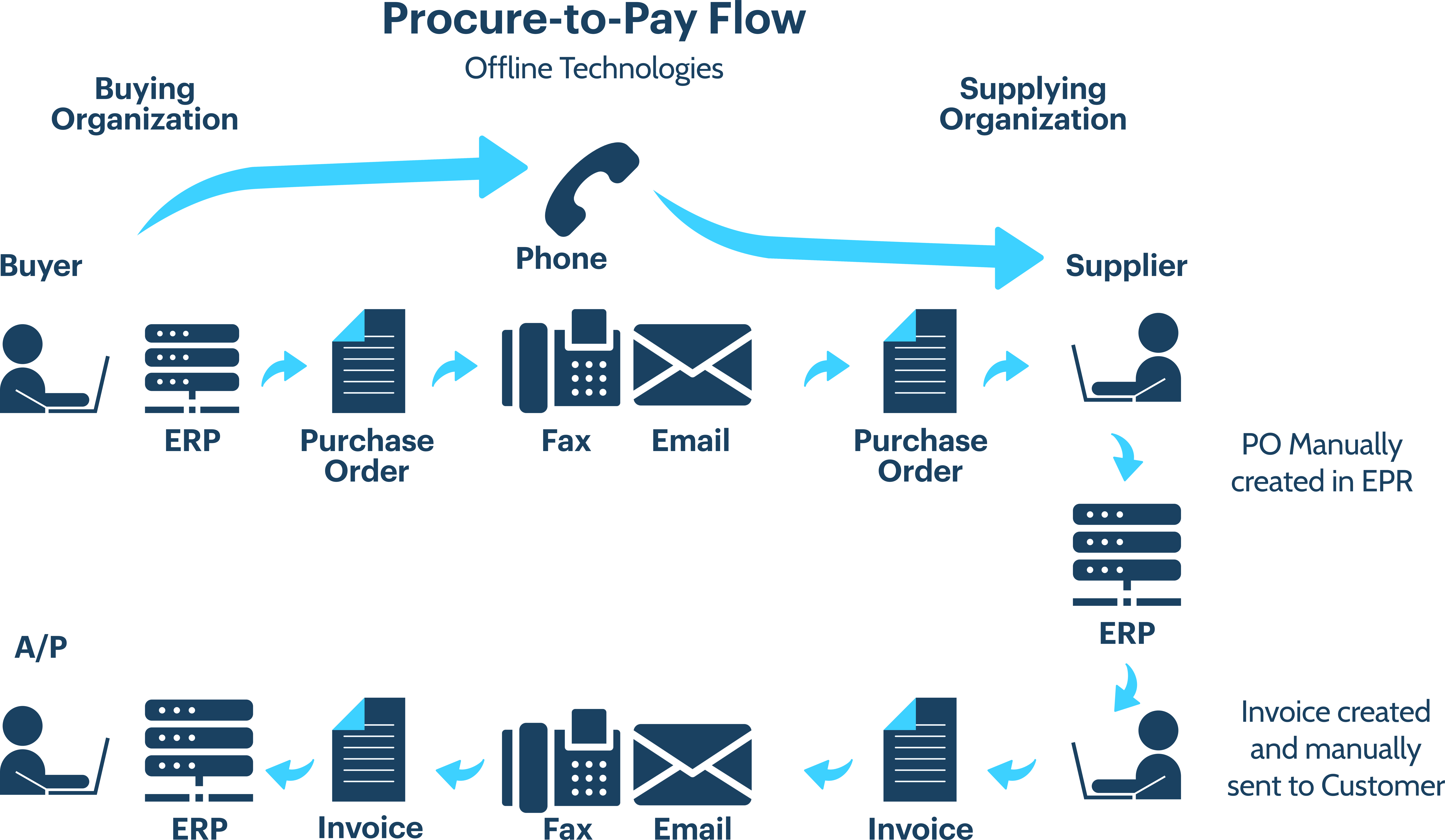
Figure A
Even in today’s digital age, many businesses continue to rely on Offline Technologies which increases cost to support business process integration which can have a dramatic negative effect on operating margins. See Benefits of EDIfor more details on business case and value proposition of EDI and related EDI programs.
Figure B refers to the same purchase order and invoice process but leveraging an automated process utilizing EDI methods of business document exchange as a manner to get a purchase order created by the buying organization into the system of the Supplying organization and a subsequent invoice triggered from the supplying organizationB
Automated System to System Based Business Process Workflow Using EDI
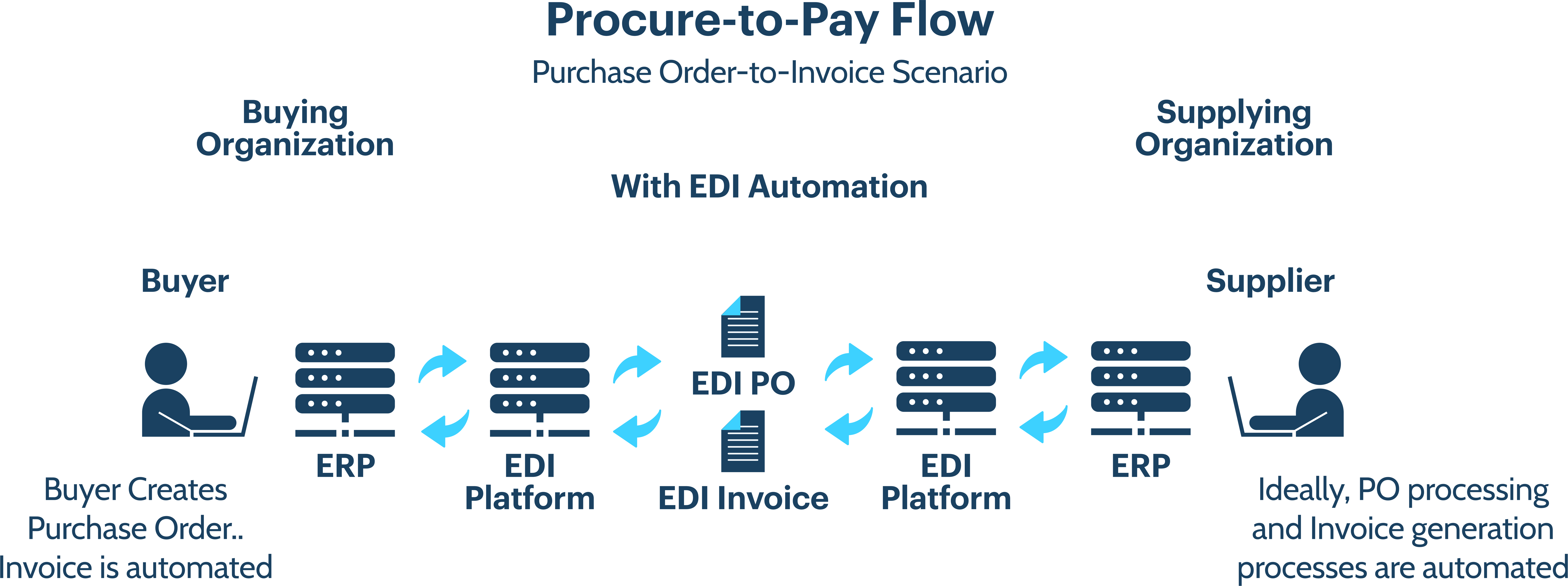
Figure B
In the automated business process flow, EDI replaced manual and offline technologies such as phone, fax, mail, and email as methods of exchange with a “system-to-system” approach to business process integration. By have the business transactions flow between sender and receiving business applications, significant efficiencies are gained and businesses mature to a “manage by exception” model and remove non value added tasks such as manual data entry from the business operation.
The world as we know it runs on and depends on EDI, a global, foundational B2B technology. While many of the core EDI standards were created 30 to 40 years ago, the emergence of Internet and secure EDI transports, coupled with the advent of Cloud EDI and Managed Service Platforms have removed many EDI barriers and allow all businesses to get the value of EDI solutions.
EDI Standards – Which Standard Should I Use?

There are over 22,000 EDI standard transactions versions in use today across the globe. There are dozens of standards, either derived by Industry, Regions, or Use Cases. Industry derivates are created to serve unique data requirements for a specific industry. For example, ANSI ASC X12 standard is the predominate industry standard in North America and the UN/EDIFACT standard is the predominate standard across Europe. HIPAA is an example of an industry standard in the Health Care industry in the United States. There are common transaction types (e.g. Purchase Order, Invoice, Advanced Shipping Notice) that are supported by the standards, and each industry has there representative standard version for the common transaction types.
These standards describe the elements of data formats and attributes while providing transaction format. Each company trading a specific transaction set with each other must have a technology that supports the standard version being traded.
See EDI Standards and Protocols for more details about the current industry standards
The following diagram depicts a representation of a paper based PO that may have been produced by a companies procurement or ERP system for delivery to a supplier. The X12 Purchase Order and EDIFACT Purchase Orders are also represented.
