The Applicability Statement 2 (AS2). Also Known as EDIINT AS2. A protocol developed by the IETF to implement secure and reliable messaging over HTTP. Allows data to be sent over the Internet using the HTTP protocol. AS2 uses the same signing, encryption, and MDN conventions used in the original AS1 protocol. AS2 messages are usually sent across the internet using the HTTP or HTTPS protocol.
AS2 has been widely deployed as a point-to-point connectivity method. AS2 offers many advantages over standard HTTP, including increased verification, and security achieved through the use of receipts and digital signatures. AS2 transactions and acknowledgements also occur in real-time, increasing the efficiency of document exchanges. Walmart was one of the first companies to help drive the adoption of AS2 across the retail sector.
Need an AS2 Solution? Learn more about our Modern EDI products and capabilities
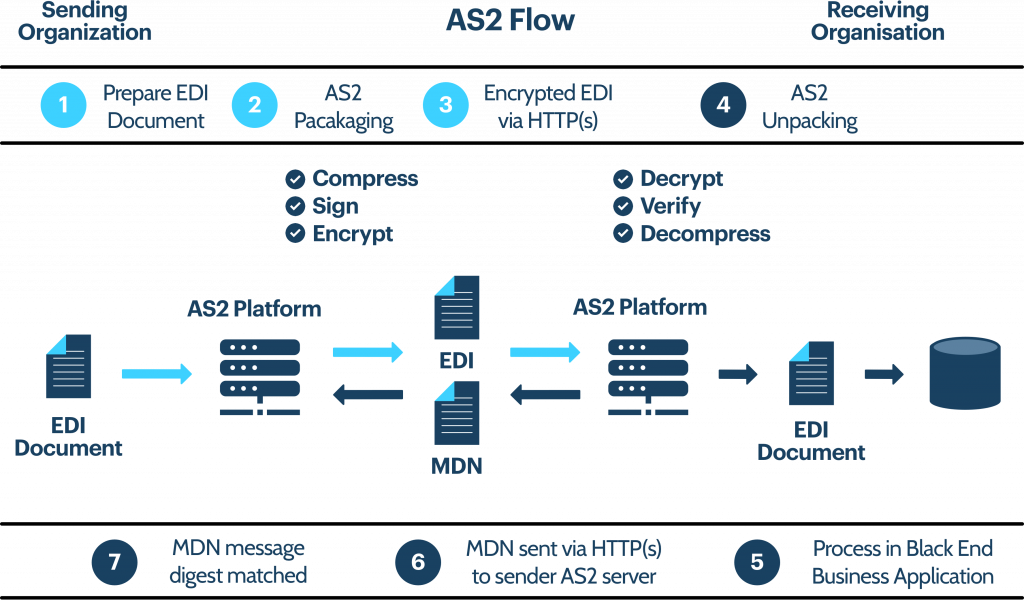
How Does AS2 work?
To establish an AS2 connection you need two computers, a server and a client. Both connect to the Internet via a point-to-point connection. In order to transmit the desired data, AS2 creates an envelope that enables secure transmission using digital certificates and encryption.
What is an AS2 MDN?
A MDN (Message Disposition Notification) is an electronic acknowledgement of receipt that is sent to the sender via AS2 after an electronic message has been sent. This acknowledgement confirms that the message has been transmitted successfully.
The MDN checks two things:
- Whether the AS2 transfer was successfully completed
- The message arrived at the desired recipient without change
The process of establishing an AS2 MDN connection is as follows:
- The sender sends an encrypted EDI message with digital signature to the desired recipient
- Transmission of the EDI message over the Internet via AS2
- Message is decrypted by the recipient and the digital signature of the sender is verified
- Recipient prepares the requested MDN and applies a digital signature. It is then sent back to the sender
- Sender receives the MDN and verifies the digital signature of the recipient
What do you need for AS2?
- AS2 Capable Software
- AS2 identifier (AS2 Name) and one certificate per partner
- Public keys of all certificates used by your AS2 partners
What are AS2 Certificates?
AS2 certificates enable the secure data exchange and security standards. Senders can generate and sign certificates, or preferably use certificates issued and verified by a trusted certificate authority. There public certificates are exchanged in advance with the partner.
AS2 Definitions
Signed Receipt- A receipt with a digital signature.
Synchronous Receipt- A receipt returned to the sender during the same HTTP session as the sender’s original message.
Asynchronous Receipt- A receipt returned to the sender on a different communication session than the sender’s original message session.
Message Disposition Notification (MDN)- The Internet messaging format used to convey a receipt. This term is used interchangeably with receipt. A MDN is a receipt.
Non-Repudiation of receipt (NRR): A “legal event” that occurs when the original sender of an signed EDI/EC interchange has verified the signed receipt coming back from the receiver. The receipt contains data identifying the original message for which it is a receipt, including the message-ID and a cryptographic hash (MIC). The original sender must retain suitable records providing evidence concerning the message content, its message-ID, and its hash value. The original sender verifies that the retained hash value is the same as the digest of the original message, as reported in the signed receipt. NRR is not considered a technical message, but instead is thought of as an outcome of possessing relevant evidence.
Non-Repudiation of Origin (NRO) – Non-repudiation is the assurance that someone cannot successfully deny the validity of something. If a trading partner has received a successful MDN, the sender cannot repudiate the fact they sent the As2 transaction.
S/MIME- A format and protocol for adding cryptographic signature and/or encryption services to Internet MIME messages.
Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS)- An encapsulation syntax used to digitally sign, digest, authenticate, or encrypt arbitrary messages.
SHA1- A secure, one-way hash algorithm used in conjunction with digital signature. This is the recommended algorithm for AS2.
MD5- A secure, one-way hash algorithm used in conjunction with digital signature. This algorithm is allowed in AS2.
MIC- The message integrity check (MIC), also called the message digest, is the digest output of the hash algorithm used by the digital signature. The digital signature is computed over the MIC.
User Agent (UA)- The application that handles and processes the AS2 request
AS2 Permutation Summary
In summary, the following twelve security permutations are possible in any given trading relationship:
1. Sender sends un-encrypted data and does NOT request a receipt.
2. Sender sends un-encrypted data and requests an unsigned receipt. Receiver sends back the unsigned receipt.
3. Sender sends un-encrypted data and requests a signed receipt. Receiver sends back the signed receipt.
4. Sender sends encrypted data and does NOT request a receipt.
5. Sender sends encrypted data and requests an unsigned receipt. Receiver sends back the unsigned receipt.
6. Sender sends encrypted data and requests a signed receipt. Receiver sends back the signed receipt.
7. Sender sends signed data and does NOT request a signed or unsigned receipt.
8. Sender sends signed data and requests an unsigned receipt. Receiver sends back the unsigned receipt.
9. Sender sends signed data and requests a signed receipt. Receiver sends back the signed receipt.
10. Sender sends encrypted and signed data and does NOT request a signed or unsigned receipt.
11. Sender sends encrypted and signed data and requests an unsigned receipt. Receiver sends back the unsigned receipt.
12. Sender sends encrypted and signed data and requests a signed receipt. Receiver sends back the signed receipt.